Porosity-Based Heterojunctions Enable Leadless Optoelectronic Modulation of Tissues
Nature Materials 2022
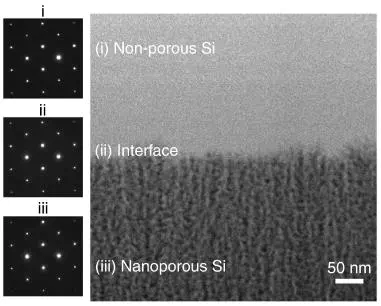
Abstract
Homo- and heterojunctions play essential roles in semiconductor-based devices such as field-effect transistors, solar cells, photodetectors and light-emitting diodes. Semiconductor junctions have been recently used to optically trigger biological modulation via photovoltaic or photoelectrochemical mechanisms. The creation of heterojunctions typically involves materials with different doping or composition, which leads to high cost, complex fabrications and potential side effects at biointerfaces. Here we show that a porosity-based heterojunction, a largely overlooked system in materials science, can yield an efficient photoelectrochemical response from the semiconductor surface. Using self-limiting stain etching, we create a nanoporous/non-porous, soft–hard heterojunction in p-type silicon within seconds under ambient conditions. Upon surface oxidation, the heterojunction yields a strong photoelectrochemical response in saline. Without any interconnects or metal modifications, the heterojunction enables efficient non-genetic optoelectronic stimulation of isolated rat hearts ex vivo and sciatic nerves in vivo with optical power comparable to optogenetics, and with near-infrared capabilities.